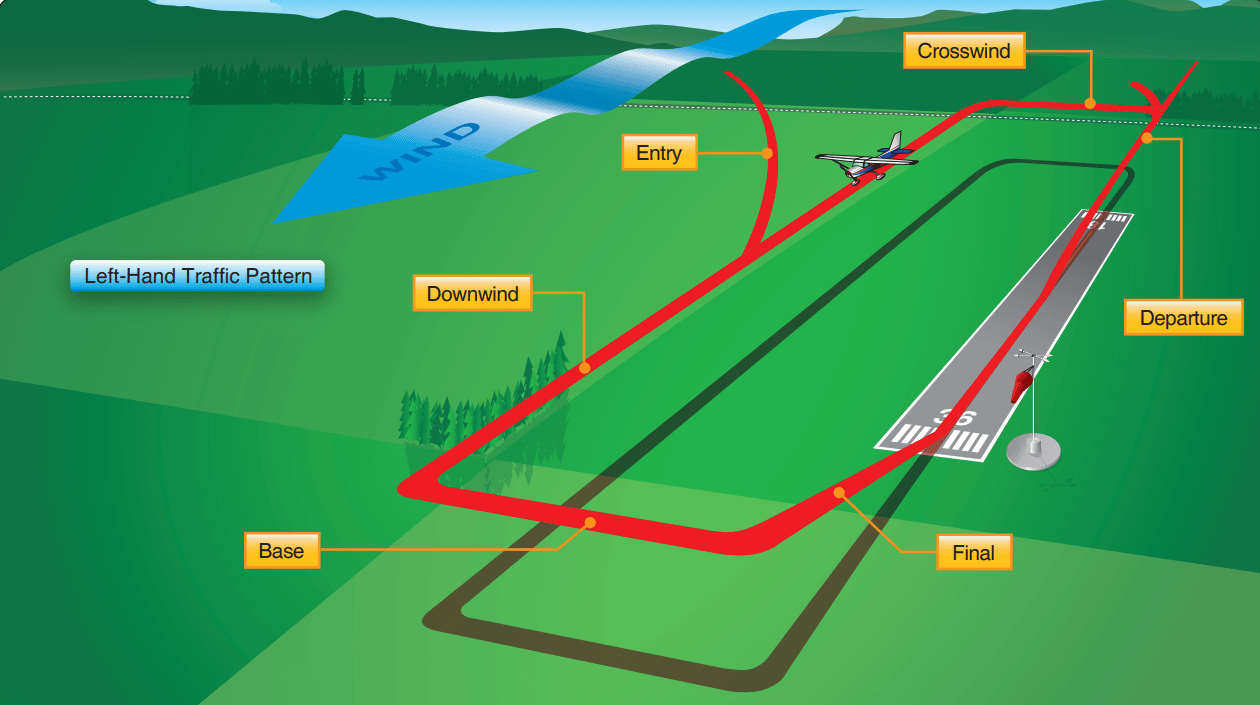
If there is a place to be overly cautious, it is in the pattern at a nontowered airport—where arriving and departing traffic mix with students making circuits for takeoff and landing practice. The use of a common altitude at a given airport is the key factor in minimizing the risk of collisions at airports without operating control towers. This tutorial explains how to fly a pattern in flightgear using the. Web the diagram below is adapted from those resources and depicts how to correctly enter and fly in the traffic pattern. Web as you pass over the airport, look at your heading indicator.
Do not dive down from a higher altitude. Web the diagram below is adapted from those resources and depicts how to correctly enter and fly in the traffic pattern. Web standard traffic pattern turns are always to the left, unless the airport specifies it otherwise. 1—enter the pattern in level flight; It will be marked on the vfr sectional, the a/fd, and if the airport has it, the traffic pattern indicator located around the windsock.
The use of a common altitude at a given airport is the key factor in minimizing the risk of collisions at airports without operating control towers. Web so, what is “the pattern”? Also, listen to the taxi instructions given to pilots of any nearby aircraft. This is the staring point from which we’ll make later adjustments. Traffic patterns are established to:
Please enter your search criteria and then click on search. Web a little refresher. A flight path parallel to the landing runway in the opposite direction of landing. Faa diagram search airport identifier: The speeds and flap settings i give are. Provide an orderly flow of air traffic at nontowered airports. This tutorial explains how to fly a pattern in flightgear using the. Web complete aeronautical information about rocky mountain metro airport (denver, co, usa), including location, runways, taxiways, navaids, radio frequencies, fbo information, fuel prices, sunrise and sunset times, aerial photo, airport diagram. Airfield traffic pattern or just pattern) is a standardized procedure to regulate the air traffic around an airport, which guarantees a safe and smooth processing of the departing and arriving traffic and also minimises the noise pollution of populated areas around the airport. Web traffic pattern operations are standardized procedures that allow pilots to arrive and depart an airfield simultaneously with others. Web traffic patterns are an essential part of every flight, and exercising good aeronautical judgment is necessary when flying them. Yet there is a surprising amount of dispute on what the lines of a pattern are actually called. We’ll start with an idealized situation. This is the staring point from which we’ll make later adjustments. The standard traffic pattern altitude is 1,000 feet above aerodrome elevation, with turbine aircraft maintaining 1,500 feet above aerodrome elevation.
For A Typical Trainer Such As A Cessna 172, A “Standard” Traffic Pattern Is Flown To The Left And At 1,000 Feet Above Ground Level (Agl).
Do not dive down from a higher altitude. Web standard traffic pattern turns are always to the left, unless the airport specifies it otherwise. Web traffic pattern operations are standardized procedures that allow pilots to arrive and depart an airfield simultaneously with others. Provide an orderly flow of air traffic at nontowered airports.
The Standard Traffic Pattern Altitude Is 1,000 Feet Above Aerodrome Elevation, With Turbine Aircraft Maintaining 1,500 Feet Above Aerodrome Elevation.
Please enter your search criteria and then click on search. All this information helps ensure the pilot is looking at the right airport diagram. This tutorial explains how to fly a pattern in flightgear using the. According to the faa , the usual numbers for such altitude are 1,000 feet or about 305 meters above the elevation of the airport ground level.
Web Airport Name And Identifier.
Web traffic patterns are an essential part of every flight, and exercising good aeronautical judgment is necessary when flying them. If there is a place to be overly cautious, it is in the pattern at a nontowered airport—where arriving and departing traffic mix with students making circuits for takeoff and landing practice. The use of a common altitude at a given airport is the key factor in minimizing the risk of collisions at airports without operating control towers. The speeds and flap settings i give are.
Web The Standard Traffic Pattern Is A Rectangular Pattern Consisting Of An Upwind, Crosswind, Downwind, And Final Approach Leg.
Unless the airport displays approved visual markings indicating that turns should be made to the right, the pilot should make all turns in the pattern to the left. This sets you on a course away from the airport directly opposite from the heading on which you will enter the pattern. This is the staring point from which we’ll make later adjustments. A flight path parallel to the landing runway in the direction of landing.